Ringworm (also known as ringworm) is a common disease caused by microscopic fungi.
It can be transmitted from person to person or acquired from the environment. The disease has different manifestations depending on the part of the body affected.
Ringworm develops when a fungus invades and multiplies the skin.
Many types of fungi and yeasts can cause this superficial skin infection. They affect different areas of the body, which is why symptoms vary. Here’s how to recognize and treat ringworm.
Symptoms of fungal skin infections
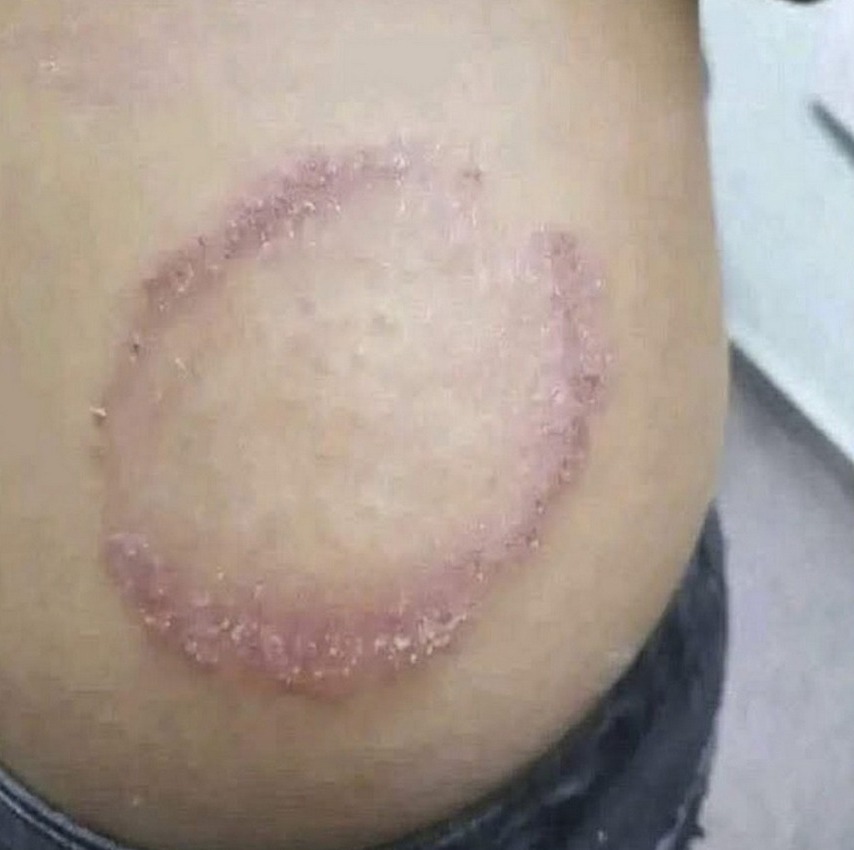
Ringworm is caused by microscopic fungi and can affect any part of the body.
Depending on the specific pathogen (dermatophytes, Candida , etc.) or type of yeast ( Malassezia , lichen variegated, etc.), as well as the site of infection, the symptoms can vary.
Early recognition is key to successful treatment.
Fungal infections most often occur on hairless areas—the face, neck, limbs, or torso.
Common symptoms include:
the appearance of red, rough spots, often ring-shaped and with a paler center;
peeling and shedding of the surface layer of the skin;
formation of small bubbles or crusts;
itching (pruritus).
Sometimes fungal infections develop in skin folds — in the groin, under the armpits, between the toes, under the breasts, behind the ears, or in the corners of the mouth.
In these cases, you may experience:
redness and inflammation;
injury and maceration of the skin (excessive moisture, making it vulnerable);
burning or pain;
scaly growth from the center to the periphery.