⸻
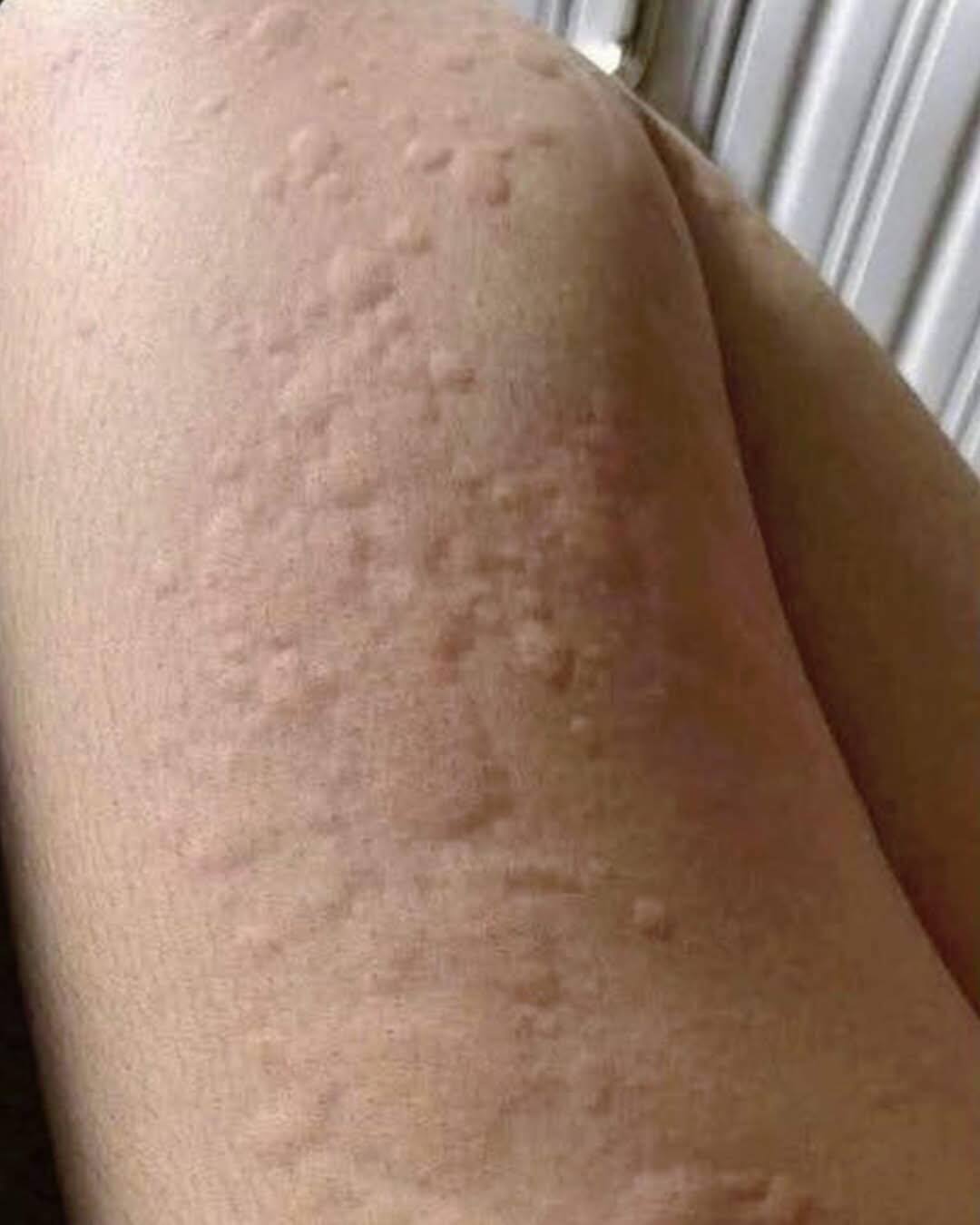
How to respond to a crisis
Goal #1 – Reduce the reaction
Mild cases: over-the-counter H1 antihistamines (loratadine, cetirizine, fexofenadine).
Moderately severe: higher doses or 2nd generation antihistamines (levocetirizine).
Complications: corticosteroids on a schedule, only under medical supervision.
Angioedema: emergency care + cold compresses.
Goal #2 – Remove the trigger
Eliminate suspicious foods for 3 to 4 weeks.
Switch to hypoallergenic cosmetics.
Review your medications with a doctor.
Reduce stress, improve sleep, breathing and relaxation techniques.
⸻
Natural home methods
Cold, wet compresses – 15–20 min.
Oatmeal baths – colloidal oatmeal in warm water.
Aloe vera – fresh leaf to refresh and soothe.
Herbs – chamomile, calendula.
Psychological support : walks, meditation, yoga.
Don’t hesitate to consult a doctor if you have any questions about dietary supplements!
⸻
Prevention
Adequate sleep, balanced diet, moderate physical activity.
Daily stress management practice – meditation, breathing, “buffers” between work and home.
Perfume-free cosmetics, clothes washed with hypoallergenic detergents.
Home medicine cabinet: antihistamine; at the doctor’s discretion – second-line medication.
In the chronic form – a check-up every 2 to 3 months.
⸻
The female perspective
Skin and emotions – keep a mood journal, include Pilates, stretching and breathing exercises.
Work-life balance : Small “switches” (a walk, soft melodies, the sound of water) signal to the skin that “everything is fine.”
Critical periods – pregnancy, postpartum period, menopause – require special vigilance and consultation with a doctor.