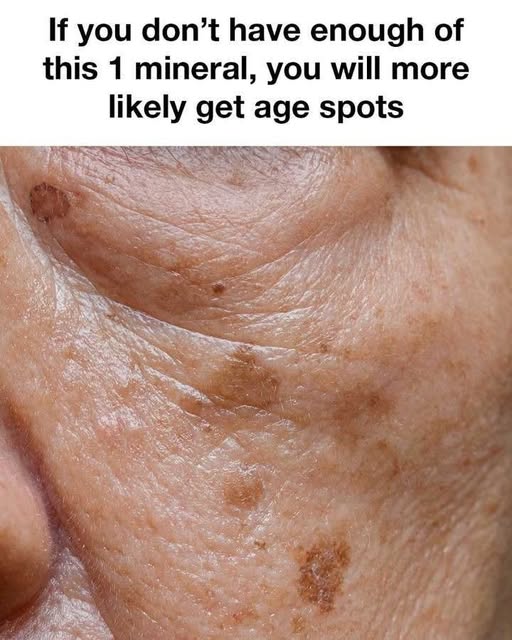
Symptoms and Signs of Selenium DeficiencySelenium deficiency can manifest in various ways, including fatigue, muscle weakness, and a weakened immune system. In terms of skin health, a deficiency may lead to increased susceptibility to sunburn, slower wound healing, and the development of age spots. Recognizing these symptoms early can help prevent further skin damage and other health issues.
How to Ensure Adequate Selenium Intake
To maintain adequate selenium levels, it’s important to consume a balanced diet that includes selenium-rich foods. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for selenium varies by age and gender, but adults generally require about 55 micrograms per day. Regularly monitoring your diet and considering supplementation if necessary can help ensure you meet these requirements.
Dietary Sources Rich in Selenium
Selenium can be found in a variety of foods, with some of the richest sources being Brazil nuts, seafood (such as tuna, halibut, and sardines), and organ meats like liver. Other good sources include eggs, sunflower seeds, and whole grains. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help you achieve optimal selenium levels.
Selenium Supplements: Benefits and Risks
While selenium supplements can be beneficial for individuals with a deficiency, it’s important to use them cautiously. Excessive selenium intake can lead to toxicity, with symptoms such as gastrointestinal distress, hair loss, and nerve damage. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation to ensure safe and appropriate use.