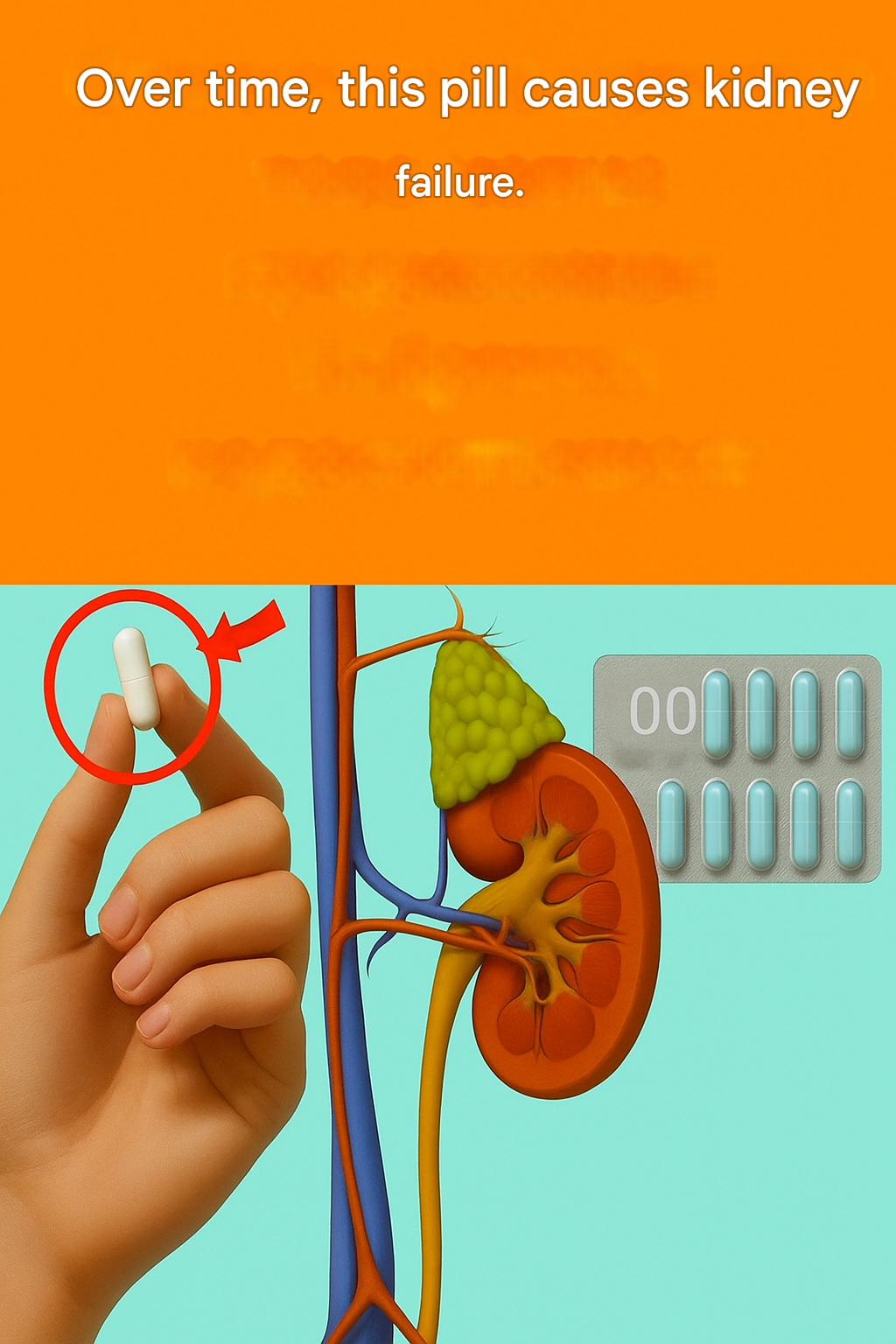
These medications can harm your kidneys – be sure to consult a doctor!
Over time, some medications can seriously damage the kidneys and even lead to kidney failure. The problem is that we often think about kidney health too late — when lab tests are already showing alarming results.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 800 million people worldwide suffer from chronic kidney disease, and in its early stages the disease can be asymptomatic. One of the most common causes of kidney damage is the improper or excessive use of medications.
Below you will find a list of commonly used drugs that, if taken for a long time or in an uncontrolled manner, can be dangerous for the kidneys.
💊 1. Omeprazole and other proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
These medications are used for heartburn, gastritis, and stomach ulcers.
Although they effectively reduce acidity, long-term use without medical supervision can cause acute or chronic kidney failure .
How to protect yourself:
Take them only on the recommendation of a gastroenterologist.
If necessary, discuss an alternative – drugs from the group of H2 blockers (famotidine, ranitidine).
⚡ 2. Ibuprofen and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Ibuprofen quickly relieves pain and fever, but it reduces blood flow to the kidneys , especially in the elderly or when dehydrated.
Prolonged use can damage tissues and lead to acute kidney failure .
Recommendation:
Do not use for more than 10 consecutive days without a doctor’s prescription.
💢 3. Painkillers: aspirin, naproxen, diclofenac
Frequent use of these medications leads to fluid retention, increased blood pressure , and in the long term, chronic kidney disease .
Symptoms of possible damage:
swelling in the limbs, nausea, fatigue, decreased urine output.
🧫 4. Antibiotics from the aminoglycoside group (gentamicin, amikacin)
These antibiotics are used for severe infections, but are toxic to nephrons , the microscopic filtering units of the kidneys.
They are prescribed only under strict medical supervision and with regular monitoring of kidney function.
⚖️ 5. Lithium (for bipolar disorder)
Lithium is effective in psychiatric conditions, but its prolonged use can disrupt water-salt balance and cause kidney failure .
Patients taking lithium should regularly visit a nephrologist and psychiatrist for monitoring of the condition.
💧 6. Diuretics (water pills)
They are used for high blood pressure and edema, but their excessive use can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance .
When the body loses too much fluid, the kidneys become overworked and cannot filter effectively.
❤️ 7. Medications to lower blood pressure
Some medications from the group of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors can reduce the filtration rate in the kidneys when taken long-term.
However, stopping these medications on their own is dangerous, as they are vital for controlling blood pressure and preventing heart complications.
✅ How to protect your kidneys
Regularly measure your blood pressure and blood sugar. These are the two main factors that affect kidney health.
Maintain a normal weight and avoid overeating.
Have a urinalysis done at least once a year — the presence of protein may be the first sign of damage.
Do not self-medicate , even if the medicine is sold without a prescription.
Limit alcohol and smoking , which put additional strain on the kidneys.
Monitor your cholesterol and triglyceride levels. High levels increase the risk of vascular disease, including kidney disease.
Drink plenty of water , unless a doctor has recommended a fluid restriction.
💡 Conclusion
The kidneys are one of the most sensitive and vital organs in the human body. Even seemingly harmless medications—painkillers, antacids, or diuretics—can cause irreversible damage to them if used incorrectly.
Before starting any course of treatment, be sure to discuss the dosage and duration with a qualified doctor . Only in this way can you be sure that the therapy will help, not harm.
This article is for informational purposes only. Do not self-medicate and always consult a qualified medical professional before applying any information from the text. The editorial team does not guarantee results and is not responsible for any damages resulting from its use.